What is Current, Voltage and Resistance? ETechBD24
Current:
Current is a flow of electrical charge carriers, usually electrons or electron-deficient atoms. The common symbol for current is the uppercase letter "I". The standard unit is the ampere, symbolized by "A".The SI unit of electrical current is the ampere, defined as 1 coulomb/second. Current is a quantity, meaning it is the same number regardless of the direction of the flow, without a positive or negative number. However, in circuit analysis, the direction of the current is relevant.
Types of Current:
The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage. These are the two main types of electrical currents.Direct Current:
Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The electric charge flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for direct current was galvanic current.Alternating Current:
In alternating current (AC, also ac), the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current, the flow of electric charge is only in one direction.Voltage:
Voltage, also called electromotive force, is a quantitative expression of the potential difference in charge between two points in an electrical field. It is measured in volts, which, technically, is the potential energy difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it. The unit "volt" is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta who invented what is considered the first chemical battery. Voltage is represented in equations and schematics by the letter "V".Types of Voltage:
Voltage can be direct or alternating. A direct voltage maintains the same polarity at all times. In an alternating voltage, the polarity reverses direction periodically. The number of complete cycles per second is the frequency, which is measured in hertz (one cycle per second), kilohertz, megahertz, gigahertz, or terahertz. An example of direct voltage is the potential difference between the terminals of an electro-mechanical cell. Alternating voltage exists between the terminals of a common utility outlet.Resistance:
Resistance is the hindrance to the flow of electrons in the material. While a potential difference across the conductor encourages the flow of electrons, resistance discourages it. The rate at which charge flows between two terminals is a combination of these two factors. The common symbol for resistance is the uppercase letter "R". The SI unit of resistance is the "Ohm".Relationship between resistance, voltage, and current:
It can be imagined from the analogy of the water tank system, that increasing the voltage in an electrical circuit will increase the level of current flowing.
Similarly, decreasing the resistance will increase the level of current as well.
In fact, there is a relationship between voltage, resistance, and current. Knowing two of the variables, it is possible to calculate the third.
The relationship between resistance, voltage, and current is known as Ohm's law and it is one of the fundamental relationships in electrical and electronic science.
- What is Current?
- What is Voltage?
- What is Resistance?
- The relation between resistance, voltage, and current.
Tags:
voltage,resistance,what is voltage,what is resistance,what is current and voltage,what is current,what is voltage and current,what is voltage current and resistance,voltage current and resistance,voltage and current,current-voltage and resistance,what is current in Hindi,what is voltage difference,what is voltage in Hindi,difference between voltage and current,what is resistance?ohms law,ohm's law,what is ohms law,what is ohm's law,ohms,law,ohm's law experiment,working of ohms law,resistance calculation of ohms law,ohms law explanation,working example of ohms law,ohm's law explained,ohm's law definition,know about ohms law,what is ohm's law explain,what is ohm's law in Hindi,ohms law wheel,example of ohms law,ohms law in Hindi,ohms law in Telugu, ETechBD24.com, ETechBD24




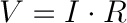





0 Comments